Epithalon upregulates telomerase activity and elongates telomeres, which has prompted research in areas including life extension, anti-aging, and the inhibition of tumorigenesis.
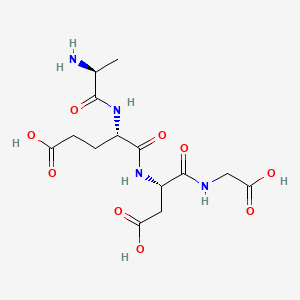
Epithalon is a synthetic tetrapeptide isolate composed of the four amino acids alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine. It is derived from epithalamin, a crude polypeptide extracted from the pineal gland [1].
The synthetic peptide was developed in the 1980s by a research team led by Professor Vladimir Khavinson of the St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology and has since been the subject of extensive research in cell cultures, animals, and humans.
Epithalon is generally available to licensed handlers, who may see it sold under names like “epitalon,” “epithalone,” and “AEDG peptide.” When sold for educational or scientific research, the peptide should be labeled as a “research chemical,” “reference material” or similar, and not intended for human use.

Epithalon upregulates telomerase activity and elongates telomeres, which has prompted research in areas including life extension, anti-aging, and the inhibition of tumorigenesis [2, 3].
Known to regulate gene expression and protein synthesis, epithalon has been found to suppress both the CCl11 and HMGB1 genes, thereby increasing the lifespan of test subjects [4].
It also has significant antioxidant effects and has been shown to inhibit carcinogenic receptor expression, which has led to research into its potential anti-tumor effects in breast and colorectal cancer [5, 6].
Epithalon has been investigated as a potential treatment for rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis due to its ability to regulate biomolecules involved in the inflammation process, such as cytokines and C-reactive protein [7].
The peptide has also been investigated as a regulator of the sleep cycle, as it increases levels of melatonin and endogenous gonadotropic hormones (FSG, LG, prolactin), which play a role in reproductive function but naturally decline with age [8].
Epithalon is classified as a research chemical outside of Russia, where it is used to treat menopause-related symptoms, anovulatory infertility, and hormone-dependent tumors [9].
As noted by the Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation (ADDF), the bulk of research involving epithalamin and epithalon has been conducted in Russia (or formerly, the Soviet Union) and has not been subject to independent confirmation [1].
The ADDF further notes that its review of epithalon has excluded roughly half of the approximately 110 epithalon/epithalamin articles published in the Russian language, though efforts have been made to refer to English translations where possible.
Below, we present a summary of key epithalon benefits based on the research available.
It is known that epithalon regulates gene expression and protein synthesis, with the general effect of reducing mortality and delaying the progression of age-associated diseases in the elderly [4].
In an in vitro study conducted by Professor Khavinson and colleagues in 2003, the team demonstrated that epithalon elongates telomeres and induces telomerase activity when introduced to telomerase-negative human fetal fibroblast cultures. The researchers concluded that epithalon may prolong the lifespan of cell populations through anti-senescence activity [2].
In a human study published that same year, Khavinson and colleagues observed that elderly human subjects who received epithalamin treatment for two to three years experienced a 1.6-1.8 fold decreased mortality rate compared with a control group. Additionally, the researchers found that the epithalamin-treated patients exhibited reduced rates of:
The researchers concluded that epithalon may be used for “health maintenance and age-related pathology prevention” in the elderly [10].
Animal studies have shown that the peptide increases melatonin may therefore enhance sleep and promote brain health.
The link between melatonin and brain health has been clarified in more recent research by Chitimus et al., noting that melatonin has antioxidant properties and can help protect the brain from oxidative stress [14].
Since oxidative stress may contribute to neurodegenerative disorders, there is strong research interest in epithalon’s role in optimizing sleep and maintaining overall brain health.
Research indicates that epithalon may be used to protect against and repair DNA damage, given its potent antioxidant activity. For example, it has been shown to:
Preclinical studies in rats and cancer-prone mice suggest that epithalon may have utility in cancer prevention.
These studies highlight the potential anti-cancer properties of eptihalon in animal models and suggest that further research in this area remains warranted.
At least two epithalamin trials have shown that the peptide is well tolerated with a favorable safety profile, and causes no severe adverse effects in test subjects [1].
According to the findings of a 15-year follow-up study on test subjects who had received up to six courses of epithalamin treatment, no adverse events were attributed to the peptide. In that study, the researchers concluded that epithalamin-treatment patients had “significantly lower mortality” than those of the control group [25].
Despite its favorable safety record, researchers should note the possibility of injection-related side effects like inflammation, itching, swelling, or pain at the site of injection. These side effects are transient and typically subside within a day or two following injection.
Researchers should follow all standard precautions to reduce the incidence of injection-related side effects, including procuring research-grade epithalon and injection supplies from a trusted source.
Epithalon injections are generally regarded as safe when administered by qualified researchers.
When administered according to clinical guidelines, epithalon presents relatively few and minor potential side effects that cease after discontinuation of treatment.
Researchers should take note of the two following risk factors:
Epithalon has not been approved outside of Russia, pending further study. Unfortunately, this has led to the illicit sale of unregulated products that are mislabeled as epithalon. Some of these products may contain harmful contaminants that can lead to systemic toxicity when injected. Avoid this by purchasing peptides from a reputable supplier.
Signs of vendor legitimacy include certificates of third-party analysis to verify peptide purity as well as relevant disclaimers against misuse. A further safety concern highlighted by the ADDF is the possibility that synthetic or isolated preparation of epithalon may constrain impurities and pose a safety risk [1].
Failure to comply with the guidelines for proper subcutaneous injections can lead to contamination and infection. Researchers must have access to sterile, high-quality supplies and adhere to standard methods of reconstitution, injection, and storage.
In sum, epithalon has been deemed safe in clinical research contexts. Nonetheless, researchers are advised to avoid excessive use and contaminants. This requires getting acquainted with the pertinent literature and following best practices when incorporating epithalon into a research study. Lastly, researchers should stay abreast of emerging literature, particularly on the long-term effects of epithalon.
Insofar as epithalon is sold as a reference material, there are no universally agreed-upon guidelines for dosing the peptide in test subjects.
Based on the work of Professor Khavinson and his research team, the International Peptide Society has published the following sample epithalon dosing protocol for anti-aging purposes (“the Russian Protocol”) [26]:
Alternatively, researchers may opt to administer an alternative protocol, involving half the total epithalon dosage, referred to in the literature as the “Ukrainian Protocol” [26]:
Researchers should note that a single 100mg epithalon course under the Russian Protocol requires two 50mg epithalon vials, while a 50mg epithalon course under the Ukrainian Protocol requires one 50mg epithalon vial.
Researchers may buy epithalon online as a research chemical from a variety of sources.
However, not all research peptide vendors sell research-grade epithalon at reasonable prices, and many fail to make good on their promises of peptide quality and purity.
At Peptideinfo.net, we know the peptide industry inside and out, having tested numerous peptide vendors and rating each based on quality, cost, and shipping.
In our experience, here is the best place to buy epithalon online:
We can confidently say that Research Peptide is an excellent vendor for any researchers who need to source peptides for research projects.
In addition to their straightforward shipping and returns process, they are accredited by the BBB and they also verify product quality using third-party lab testing.
Here’s more about why we like working with Research Peptide:
Not only that, this vendor is also one of a few that offers Epithalon capsules for research.
In addition, they’re offering qualified researchers 10% off their next Research Peptide order. Just follow the link below and add this code:

Epithalon is available in lyophilized powder form, which must be reconstituted with bacteriostatic or sterile water. Additionally, epithalon is available in nasal spray form.
Following reconstitution with bacteriostatic water or sterile water, epithalon is administered subcutaneously.
Epithalon is reconstituted with bacteriostatic water or sterile water. To reconstitute epithalon, drip the desired amount of bacteriostatic water down the side of the epithalon vial, allowing the solution to dissolve on its own.
As an uncontrolled and non-prescription substance, epithalon is generally legal to buy, sell, and handle for educational or scientific research conducted by qualified professionals. In the United States, epithalon may not be marketed to the public as a medicinal product due to its lack of approval by the US Food and Drug Administration.
No. Epithalon researchers have demonstrated the peptide’s long-term safety and efficacy. Epithalon administration is associated with minor injection-related side effects, and severe adverse reactions are extremely rare.
Yes. Epithalon has been studied extensively since the 1980s and is known to offer important anti-aging, sleep-promoting, and disease-fighting benefits via telomere elongation.
No. Epithalon is not an anabolic-androgenic steroid. It is a telomerase activator and a synthetic version of the polypeptide epithalamin.
No. Epithalon is not known to increase testosterone.
No. Epithalon is not known to play any role in muscle building.
No. Epithalon is not known to cause weight gain.
Epithalon has demonstrated anti-aging, sleep-promoting, and disease-fighting benefits and may be of interest to peptide researchers actively working in these areas.
With its excellent safety profile and ease of administration, epithalon may be administered twice annually in two short courses for its anti-aging effects.
Visit our top recommended supplier to obtain high-purity epithalon for research.
Disclaimer: Peptideinfo.net contains information about products that are intended for laboratory and research use only, unless otherwise explicitly stated. This information, including any referenced scientific or clinical research, is made available for educational purposes only. Peptideinfo.net makes every effort to ensure that any information it shares complies with national and international standards for clinical trial information and is committed to the timely disclosure of the design and results of all interventional clinical studies for innovative treatments publicly available or that may be made available. However, research is not considered conclusive. Peptideinfo.net makes no claims that any products referenced can cure, treat or prevent any conditions, including any conditions referenced on its website or in print materials.
To the extent that Peptideinfo.net references a product that is also a prescription medication, Peptideinfo.net does not does not offer medical diagnosis or treatment advice. The contents of Peptideinfo.net are intended exclusively for qualified researchers. Any individual seeking any advice on any prescription medication, or any disease or condition, is advised to refrain from using this site and consult their healthcare provider. Statements regarding products presented on Peptideinfo.net are the opinions of the individuals making them and are not necessarily the same as those of Peptideinfo.net.
Your access to Peptideinfo.net is subject to our terms of use.